Abstract
Case Report
Laparoscopic-Assisted Transumbilical Extracorporeal Resection of Meckel’s Diverticulum in 10 years old boy with symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding
Karavdić K*, Firdus A, Mešić A, Rahmanović S, Milardović R and Đuran A
Published: 20 April, 2020 | Volume 4 - Issue 1 | Pages: 006-010
The Meckel’s diverticulum (MD) is the most common anomaly of ductus omphaloentericus that surgeon encounters in clinical practice. The accurate incidence is unknown because most patients with the Meckel’s diverticulum are asymptomatic. Most studies report an incidence of about 2%. Approximately 4% of patients with the Meckel’s diverticulum become symptomatic.
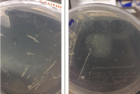
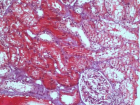
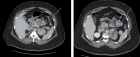
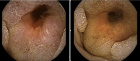
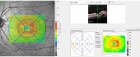
A 10 years old boy, was sent from regional hospital. His symptoms started the day before he was hospitalized and represented as gastrointestinal bleeding, lower abdominal pain and four times vomiting, without fever. Ultrasound and X-ray of the abdomen were normal. Blood findings showed: RBC 3,19, hemoglobin 0,95, hematocrit 0,27. During a physical examination abdomen was palpatory soft, with no presence of the pain. Digital rectal examination showed blood. A scintigraphy pathologic scan showed a focal lesion of the right hemi abdomen consistent with the Meckel’s diverticulum.Patient was treated byLaparoscopic-Assisted Transumbilical Extracorporeal Resection of the Meckel’s Diverticulum.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001044 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Diverticulum; Meckel; Laparascopic; Extracorporeal
References
- Chan KW, Lee KH, Wong HY, Tsui SY, Wong YS, et al. Laparoscopic excision of Meckel's diverticulum in children:What is the current evidence? World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20: 15158-15162. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25386065
- Papparella A, Nino F, Noviello C, Marte A, Parmeggiani P, et al. Laparoscopic approach to Meckel's diverticulum. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20: 8173-8178. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25009390
- Prasad TR, Chui CH, Jacobsen AS. Laparoscopic-Assisted Resection of Meckel’s Diverticulum in Children. JSLS. 2006; 10: 310–316. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17212886
- Varcoe RL, Wong SW, Taylor CF, Newstead GL.Diverticulectomy is indequate treatment for short Meckel’s diverticulum with heterotopic mucosa. ANZ J Surg. 2004; 74: 869-872. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15456435
- Vane DW, West KW, Grosfeld JL. Vitelline duct anomalies. Experience with 217 childhood cases. Arch Surg. 1987; 122: 542-547. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3495250
- Sai Prasad TR, Chui CH, Singaporewalla FR, Ong CP, Low Y, et al. Meckel’s diverticular complications in children: is laparoscopy the order of the day? Pediatr Surg Int. 2007; 23: 141-147. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17171378
- Menezes M, Tareen F, Saeed A, Khan N, Puri P. Symptomatic Meckel’s diverticulum in children: a 16-year review. Pediatr Surg Int. 2008; 24: 575-577. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18322689
- Rashid OM, Ku JK, Nagahashi M, Yamada A, Takabe K. Inverted Meckel’s diverticulum as a cause of occult lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18: 6155-6159. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23155346
- Palanivelu C, Rangarajan M, Senthilkumar R, Madankumar MV, Kavalakat AJ. Laparoscopic management of symptomatic Meckel’s diverticula: a simple tangential stapler excision. JSLS 2008; 12: 66-70. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18402742
- Teitelbaum DH, Polley TZ Jr, Obeid F. Laparoscopic diagnosis and excision of Meckel’s diverticulum. J Pediatr Surg. 1994; 29: 495-497. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8014801
- Schier F, Hoffmann K, Waldschmidt J. Laparoscopic removal of Meckel’s diverticula in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1996; 6: 38-39. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8721178
- Chan KW, Lee KH, Mou JW, Cheung ST, Tam YH. Laparoscopic management of complicated Meckel’s diverticulum in children: a 10-year review. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22: 1509-1512. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18322735
- Shalaby RY, Soliman SM, Fawy M, Samaha A. Laparoscopic management of Meckel’s diverticulum in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2005; 40: 562-567. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15793736
- Ng WT, Wong MK, Kong CK, Chan YT. Laparoscopic approach to Meckel’s diverticulectomy. Br J Surg. 1992; 79: 973-974. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1422773
- Attwood SE, McGrath J, Hill AD, Stephens RB. Laparoscopic approach to Meckel’s diverticulectomy. Br J Surg. 1992; 79: 211. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1532525
- Altinli E, Pekmezci S, Gorgun E, Sirin F. Laparoscopy-assisted resection of complicated Meckel’s diverticulum in adults. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2002; 12: 190-194. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12080263
- Park JJ, Wolff BG, Tollefson MK, Walsh EE, Larson DR.. Meckel diverticulum: the Mayo Clinic experience with 1476 patients (1950-2002). Ann Surg. 2005; 241: 529-533. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15729078
- Amoury R, Snyder C. Meckel’s diverticulum. Pediatric surgery. Louis: Mosby, St., 1988; 1173-1184.
- Sai Prasad TR, Chui CH, Singaporewalla FR, Ong CP, Low Y, et al. Meckel’s diverticular complications in children: is laparoscopy the order of the day? Pediatr Surg Int. 2007; 23: 141-147. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17171378
- Teitelbaum DH, Polley TZ Jr, Obeid F. Laparoscopic diagnosis and excision of Meckel’s diverticulum. J Pediatr Surg. 1994; 29: 495-497. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8014801
Figures:

Figure 1

Figure 2
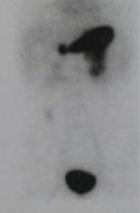
Figure 3
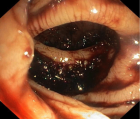
Figure 4
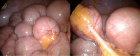
Figure 5
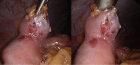
Figure 6
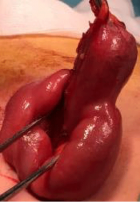
Figure 7
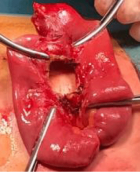
Figure 8
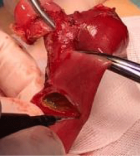
Figure 9
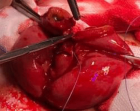
Figure 10
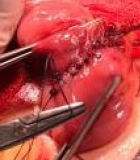
Figure 11
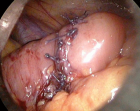
Figure 12
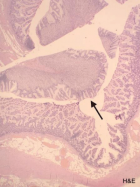
Figure 13
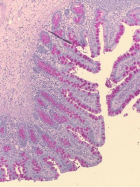
Figure 14
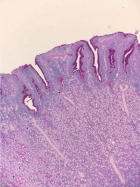
Figure 15
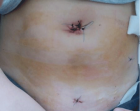
Figure 16
Similar Articles
-
Massive gastrointestinal bleeding; never too old to be due to Meckel’s Diverticulum - A case report and literature reviewSubhi Mansour,Kenan Halloun,Safi Khuri*. Massive gastrointestinal bleeding; never too old to be due to Meckel’s Diverticulum - A case report and literature review. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001030; 3: 034-039
-
Laparoscopic-Assisted Transumbilical Extracorporeal Resection of Meckel’s Diverticulum in 10 years old boy with symptoms of gastrointestinal bleedingKaravdić K*,Firdus A,Mešić A,Rahmanović S,Milardović R,Đuran A. Laparoscopic-Assisted Transumbilical Extracorporeal Resection of Meckel’s Diverticulum in 10 years old boy with symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001044; 4: 006-010
Recently Viewed
-
Clinical and Histopathological Mismatch: A Case Report of Acral FibromyxomaMonica Mishra*,Kailas Mulsange,Gunvanti Rathod,Deepthi Konda. Clinical and Histopathological Mismatch: A Case Report of Acral Fibromyxoma. Arch Pathol Clin Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001045; 9: 005-007
-
Unconventional powder method is a useful technique to determine the latent fingerprint impressionsHarshita Niranjan,Shweta Rai,Kapil Raikwar,Chanchal Kamle,Rakesh Mia*. Unconventional powder method is a useful technique to determine the latent fingerprint impressions. J Forensic Sci Res. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001035; 6: 045-048
-
Doppler Evaluation of Renal Vessels in Pediatric Patients with Relapse and Remission in Different Categories of Nephrotic SyndromeAmit Nandan Dhar Dwivedi*, Srishti Sharma, OP Mishra, Girish Singh. Doppler Evaluation of Renal Vessels in Pediatric Patients with Relapse and Remission in Different Categories of Nephrotic Syndrome. J Clini Nephrol. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001112; 7: 067-072
-
Atlantoaxial subluxation in the pediatric patient: Case series and literature reviewCatherine A Mazzola*,Catherine Christie,Isabel A Snee,Hamail Iqbal. Atlantoaxial subluxation in the pediatric patient: Case series and literature review. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001037; 4: 069-074
-
Intelligent Design of Ecological Furniture in Risk Areas based on Artificial SimulationTorres del Salto Rommy Adelfa*, Bryan Alfonso Colorado Pástor*. Intelligent Design of Ecological Furniture in Risk Areas based on Artificial Simulation. Arch Surg Clin Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001083; 8: 062-068
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."