Abstract
Case Report
Laparoscopic approach for acute right iliac fossa pathology: Our experience
Luciano Onofrio* and Gianfausto Iarrobino
Published: 31 December, 2020 | Volume 4 - Issue 2 | Pages: 054-058
Laparoscopic approach in emergency theatre is an irreplaceable tool to manage patients with acute surgical pathology. We retrospectively reviewed surgical access records from the Emergency Department for acute right iliac fossa pathology. We considered 51 patients (16 male, 35 female, mean age 23.8 years) access for acute right iliac fossa pathology over the last year. 44 patients underwent laparoscopic approach (86%); 8 patients were treated with an open approach. Outcomes evaluation was based on data comparison from open appendicectomy over 4 year time period.
Variables considered for data analyses were: role of laparoscopic surgery for gangrenous/perforated appendicitis, Conversion rate, Laparoscopy appendicectomy for elderly patients.
Our study demonstrated that a laparoscopic approach at acute right iliac fossa pathology is feasible, safe and can offer a low incidence of infectious complications, less post-operative pain, rapid recovery, and represent a valid diagnostic tool in doubtful cases, at the expense of longer operating time than OA. We suggest that LA should be the initial choice for all patients with acute right iliac fossa pathology.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001055 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Laparoscopic appendicectomy; Abdominal pain; Right iliac fossa; Complicated appendicectomy
References
- Adiss DG, Shaffer N, Fowler BS, Tauxe RV. The epidemiology of appendicitis and appendectomy in the United States. 1990; 132: 910-925. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2239906/
- Gans SL, Pols MA, Stoker J, Boermeester MA. Expert steering group. Guideline for the Diagnostic Pathway in Patients with Acute Abdominal Pain. Digest Surg. 2015; 32: 23-31. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25659265/
- Cariati A, Brignole E, Tonelli E, Filippi M, Guasone F, et al. Laparoscopic or open appendectomy. Critical review of the literature and personal experience. G Chir. 2001; 22: 353-357. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11816948/
- Arias MP, Barreira AS, Sánchez MM, Eire PF, Saavedra SG, et al. Appendicitis versus non-specific acute abdominal pain: Paediatric Appendicitis Score evaluation. An Pediatr. 2018; 88: 32-38. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28254168/
- Gans SL, Pols MA, Stoker J, Boermeester MA. Expert steering group. Guideline for the diagnostic pathway in patients with acute abdominal pain. Dig Surg. 2015; 32: 23-31. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25659265/
- Onur OE., et al. Follow-up ambulatoriale o “osservazione clinica attiva” in pazienti con dolore addominale aspecifico in pronto soccorso. Uno studio clinico randomizzato. Minerva Chirurgica. 2008; 63: 9-15.
- Royds Jones HM. The False "Acute Abdomen". 1951.
- Rathish D, Karalliyadda S. Concurrent presentation of thyroid storm and diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review of previously reported cases. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019; 19: 49. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31101104/
- Vetshev PS, Ippolitov LI, KOvalenko EI. False acute abdomen in clinical practice. Klin Med (Mosk). 2003; 81: 20-27.
- Ruffolo C, Fiorot A, Pagura G, Antoniutti M, Massani M, et al. Acute appendicitis: What is the gold standard of treatment? World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19: 8799–8807. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24379603/
- Lin HF, Lai HS, Lai IR. Laparoscopic treatment of perforated appendicitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20: 14338–14347. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4202363/
- Jaschinski T, Mosch CG, Eikermann M, Neugebauer EAM, Sauerland S Laparoscopic versus open surgery for suspected appendicitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018; 11: CD001546. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30484855/
- Melanie B, Saltzman DA, Rosen JI, Acton RD, Segura BJ, et al. Standardized irrigation technique reduces intraabdominal abscess after appendectomy. J Pediat Surg. 2019; 54: 728-732. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30025605/
- Domene CE, Volpe P, Heitor FA. Three port laparoscopic appendectomy technique with low cost and aesthetic advantage. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2014; 27(Suppl 1): 73–76. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25409972/
- Guller U, Hervey S, Purves H, Muhlbaier LH, Peterson ED, et al. Laparoscopic Versus Open Appendectomy: Outcomes Comparison Based on a Large Administrative Database. Ann Surg. 2004; 239: 43-52. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14685099/
- Lim SG, Ahn EJ, Kim SY, Chung Y ll, Park JM, et al. A Clinical Comparison of Laparoscopic versus Open Appendectomy for Complicated Appendicitis. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2011; 27: 293-297. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3259425/
- Sakpal SV, Bindra SS, Chamberlain RS. Laparoscopic appendectomy conversion rates two decades later: an analysis of surgeon and patient-specific factors resulting in open conversion. J Surg Res. 2012; 176: 42-49. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21962732/
- Wang D, Dong T, Shao Y, Gu T, Xu Y, et al. Laparoscopy versus open appendectomy for elderly patients, a meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Surgy. 2019; 19: 54.
- Kirshtein B, Perry ZH, Mizrahi S, Lantsberg L. Value of laparoscopic appendectomy in the elderly patient. World J Surg. 2009; 33: 918-922. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19172345/
- Decadt B, Sussman L, Lewis MP, Secker A, Cohen L, et al. Randomized clinical trial of early laparoscopy in the management of acute non-specific abdominal pain. Br J Surg. 1999; 86: 1383-1386. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10583282/
- Viniol A, Keunecke C, Biroga T, Stadje R, Dornieden K, et al. Studies of the symptom abdominal pain--a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fam Pract. 2014; 31: 517–529. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24987023/
- Sapmaz F, Başyiğit S, Başaran M, Demirci S. Non-Surgical Causes of Acute Abdominal Pain - Actual Problems of Emergency Abdominal Surgery. 2016.
- Peedikathara LM, Mandumpala JM, Vallon SM, Kavalakat AJ. Predictors for conversion to open appendicectomy in patients undergoing laparoscopic appendicectomy: a prospective study. Int Surg J. 2018; 5: 2588-2594.
- Malý O, Páral J. Appendicitis as a rare cause of mechanical small-bowel obstruction: A literature review of case reports. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016; 29: 180-184. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27865147/
- Kothadia JP, Katz S, Ginzburg L. Chronic appendicitis: uncommon cause of chronic abdominal pain. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2015; 8: 160–162. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25949528/
- See TC, Watson CJE, Arends MJ, Ng CS. Atypical appendicitis: the impact of CT and its management. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2008; 52: 140-147. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18373805/
Figures:
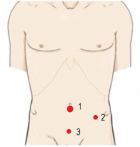
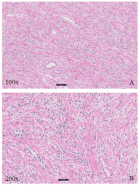
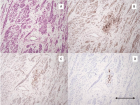
Figure 1
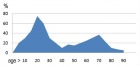
Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
Gossypiboma due to a retained surgical sponge following abdominal hysterectomy, complicated by intestinal migration and small bowel obstruction- A Case ReportVivek Agrawal,Praroop Gupta*. Gossypiboma due to a retained surgical sponge following abdominal hysterectomy, complicated by intestinal migration and small bowel obstruction- A Case Report. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001017; 2: 015-017
-
Actinomycosis of the appendixLucas Wheatley*,Michael Lonne,James Bennnet,Bhavik Patel. Actinomycosis of the appendix. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001020; 2: 029-030
-
A successful case report in woman: A gender medicine?Emilio Laviscio,Tiziana Ciarambino*,Annita Imbriani,Mauro Giordano,Filippo Topo. A successful case report in woman: A gender medicine?. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001029; 3: 032-033
-
Acute Appendicitis: Hispanics and the Hamburger SignGarcia Gubern C,Colon Rolón L,Ruiz Mercado I,Oliveras Garcia C,Caban Acosta D,Muñoz Pagán J,Iriarte I,Bolaños Ávila G,Peguero Rivera J,Sánchez Gaetan F,Oneill Castro J, Cordero Colón Paola N,Garcia-Colon Carlos A,Romero-Vazquez Ana M*. Acute Appendicitis: Hispanics and the Hamburger Sign. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001041; 3: 078-081
-
Lateral Pancreato-Jejunostomy in Chronic Pancreatitis: An appraisal of 32 casesSardar Rezaul Islam*,Shafiqur Rahman,Shaurav Talukdar,Shah Alam Sarkar,Shah Poran,Mushfiqur Rahman. Lateral Pancreato-Jejunostomy in Chronic Pancreatitis: An appraisal of 32 cases. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001043; 4: 001-005.
-
Laparoscopic-Assisted Transumbilical Extracorporeal Resection of Meckel’s Diverticulum in 10 years old boy with symptoms of gastrointestinal bleedingKaravdić K*,Firdus A,Mešić A,Rahmanović S,Milardović R,Đuran A. Laparoscopic-Assisted Transumbilical Extracorporeal Resection of Meckel’s Diverticulum in 10 years old boy with symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001044; 4: 006-010
-
Acute necrotising pancreatitis masquerading as psoas abscess: A report of two casesPraveenkumar M Patil*,Kartik Sharma,Navneet Kaur. Acute necrotising pancreatitis masquerading as psoas abscess: A report of two cases. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001046; 4: 018-021
-
Laparoscopic approach for acute right iliac fossa pathology: Our experienceLuciano Onofrio*,Gianfausto Iarrobino. Laparoscopic approach for acute right iliac fossa pathology: Our experience. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001055; 4: 054-058
-
Coexistence of common gallstones and sinusoidal obstruction syndrome: Case report and review of the literatureFurkan Karahan*,Nihan Acar,Arzu Avcı,Osman Nuri Dilek. Coexistence of common gallstones and sinusoidal obstruction syndrome: Case report and review of the literature. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001060; 5: 020-022
-
Chronic Pancreatitis with Stones: What is the Best Way to Treat?Joseph Boujaoude,Rose Al Bacha,Bassam Abboud. Chronic Pancreatitis with Stones: What is the Best Way to Treat?. . 2025 doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001086; 9: 017-024
Recently Viewed
-
The Synergistic Effect of Combined Linagliptin and Metformin Improves Hepatic Function in High-fat Diet/Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic RatsFolasade Omobolanle Ajao*,Ifedolapo Opeyemi Adeyeye,Noheem Olaoluwa Kalejaiye,Sodik Olasunkami Mukaila,Olalekan Samson Agboola,Marcus Olaoye Iyedupe. The Synergistic Effect of Combined Linagliptin and Metformin Improves Hepatic Function in High-fat Diet/Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001050; 9: 004-012
-
Schizoaffective Disorder in an Individual with Mowat-Wilson Syndrome (MWS)Yadwinder Chuhan, Nimrit Bath, Muhammad Ayub*. Schizoaffective Disorder in an Individual with Mowat-Wilson Syndrome (MWS). Arch Psychiatr Ment Health. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apmh.1001050; 8: 008-011
-
Clinical Severity of Sickle Cell Anaemia in Children in the Gambia: A Cross-Sectional StudyLamin Makalo,Samuel A Adegoke,Stephen J Allen,Bankole P Kuti,Kalipha Kassama,Sheikh Joof,Aboulie Camara,Mamadou Lamin Kijera,Egbuna O Obidike. Clinical Severity of Sickle Cell Anaemia in Children in the Gambia: A Cross-Sectional Study. J Hematol Clin Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jhcr.1001033; 9: 001-006
-
Prospective evaluation of a computerized algorithm for Vitamin K antagonist drug dose calculationMaarten J Beinema*,Jacobus RBJ Brouwers,Henk Adriaansen,Frank GA Jansman. Prospective evaluation of a computerized algorithm for Vitamin K antagonist drug dose calculation. J Hematol Clin Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jhcr.1001020; 7: 001-005
-
Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma presenting as renal crisis, a case report and review of the literatureUrvi V Patel, Navdeep Sangha*, Andrew Rettew. Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma presenting as renal crisis, a case report and review of the literature. J Hematol Clin Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jhcr.1001021; 7: 001-010
Most Viewed
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic ReviewMohammad Hossein Karami*, Majid Abdouss*, Mandana Karami. Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001151; 6: 201-215
-
Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available KnowledgeAvishek Mandal*. Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available Knowledge. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001039; 7: 001-010
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."